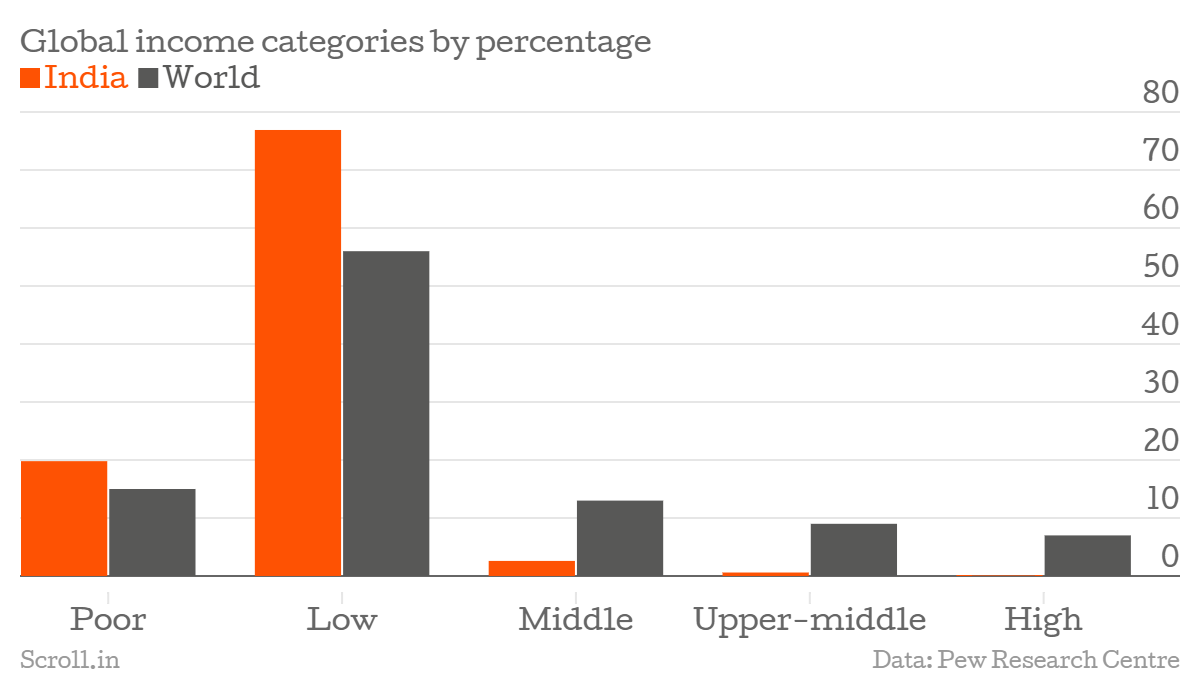
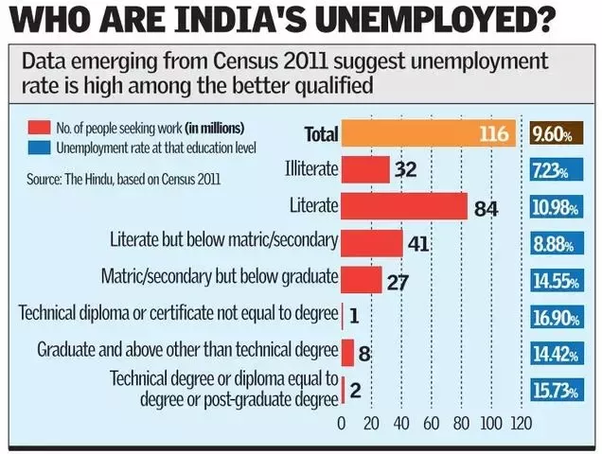
Being a poor country and one of the fastest growing economies in the world, there are some unique economic issues in India as explained below:
Low per capita income
Usually, developing economies have a low per-capita income. The per capita income in India in 2014 was $1,560. In the same year, the per-capita Gross National Income (GNI) of USA was 35 times that of India and that of China was 5 times higher than India.
Further, apart from the low per-capita income, India also has a problem of unequal distribution of income. This makes the problem of poverty a critical one and a big obstacle in the economic progress of the country. Therefore, low per-capita income is one of the primary economic issues in India.
Huge dependence of population on agriculture
Another aspect that reflects the backwardness of the Indian economy is the distribution of occupations in the country. The Indian agriculture sector has managed to live up to the demands of the fast-increasing population of the country.
According to the World Bank, in 2014, nearly 47 percent of the working population in India was engaged in agriculture. Unfortunately, it contributed merely 17 percent to the national income implying a low productivity per person in the sector. The expansion of industries failed to attract enough manpower either.

????????????????????????????????????
Heavy population pressure
Another factor which contributes to the economic issues in India is population. Today, India is the second most-populated country in the world, the first being China.
We have a high-level of birth rates and a falling level of death rates. In order to maintain a growing population, the administration needs to take care of the basic requirements of food, clothing, shelter, medicine, schooling, etc. Hence, there is an increased economic burden on the country.
The existence of chronic unemployment and under-employment
The huge unemployed working population is another aspect which contributes to the economic issues in India. There is an abundance of labor in our country which makes it difficult to provide gainful employment to the entire population.
Also, the deficiency of capital has led to the inadequate growth of the secondary and tertiary occupations. This has further contributed to chronic unemployment and under-employment in India.
With nearly half of the working population engaged in agriculture, the marginal product of an agricultural laborer has become negligible. The problem of the increasing number of educated-unemployed has added to the woes of the country too.
Inequality in wealth distribution
According to Oxfam’s ‘An economy for the 99 percent’ report, 2017, the gap between the rich and the poor in the world is huge. In the world, eight men own the same wealth as the 3.6 billion people who form the poorest half of humanity.
In India, merely 1 percent of the population has 58 percent of the total Indian wealth. Also, 57 billionaires have the same amount of wealth as the bottom 70 percent of India. Inequal distribution of wealth is certainly one of the major economic issues in India.
Lack of access to basic amenities
In 2011, according to the Census of India, nearly 7 percent of India’s population lives in rural and slum areas. Also, only 46.6 percent of households in India have access to drinking water within their premises. Also, only 46.9 percent of households have toilet facilities within the household premises.
This leads to the low efficiency of Indian workers. Also, dedicated and skilled healthcare personnel are required for the efficient and effective delivery of health services. However, ensuring that such professionals are available in a country like India is a huge challenge.
Conclusion-
Apart from these common issues there are various other issues which builds up into the problem and restrict India’s growth.Issues like women security, increase rate of Rape and domestic violence, Naxalism and child health care with education are some of them.
Author-
Raman Tirpude
MBA,BE (student)